NB-IoT is a new wireless standard developed for low-power, low-cost IoT devices that works with cellular infrastructure. Its low power consumption, long-distance characteristics, and powerful signal penetration provide the benefits of other wireless technologies in a specific environment. As a result, NB-IoT is the ideal choice for IoT devices to link to the cloud.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the "last mile" problem. While the cloud infrastructure used to collect and analyze data is already in place, the wireless infrastructure that can now be used to link a large number of devices to the network with both transmission distance, low power and low cost is not yet in place.
The narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) is a new wireless standard developed for low-power, low-cost IoT devices that works with cellular infrastructure. No dedicated gateway is required, so device manufacturers can focus on designing the functionality of the device without worrying about wireless infrastructure issues.

Figure 1 NB-IoT technical characteristics
As a narrowband radio technology, the NB-IoT features low power consumption, long range, and powerful signal penetration to provide advantages not found in other wireless technologies in a specific environment (Figure 1). Combining these advantages with the support of the mobile communications industry makes NB-IoT an ideal choice for linking IoT devices to the cloud. After years of development, the NB-IoT standard was finalized in June 2016 and became part of the 13th edition of the 3GPP. It is a narrowband technology that uses only 180kHz bandwidth. Therefore, its data transfer rate is only about 27.2kbit/s download and 62.5kbit/s upload. Although this amount of transmission is much lower than Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or high-end cellular technology, it is more than enough for many IoT applications that only need to transmit status information.
With power, distance, penetration advantages
Since the NB-IoT link uses only a small bandwidth, it can realize long-distance communication with low power consumption. In addition, the narrow frequency plus the operation of the frequency band below GHz means that the NB-IoT has excellent signal penetration. Also because it uses licensed bands, NB-IoT has better signal integrity and lower interference than Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and other communication protocols operating on the increasingly tamper-free ISM license-free band.
Although NB-IoT is designed with the cellular network provider, the hardware is compatible with the existing network, but in fact, it is a brand new communication protocol, not the same as the existing LTE or 3G protocol. As a "new design" standard, the NB-IoT stack is simple and easy to implement, which means that the NB-IoT radio module is much simpler and more cost-effective than most cellular radios.
Unlike other competing IoT wireless protocols that rely on gateways, the cellular nature of NB-IoT means that designers can connect to the Internet simply by adding NB-IoT radio modules to their devices as long as they are supported by local network vendors. No gateway or router at all. For many companies, this simplifies development costs and speeds time-to-market, as long as they focus on their core competencies without having to spend the effort to build a wireless infrastructure that supports their IoT deployment.
NB-IoT application field diversity
Although NB-IoT did not complete the standard setting in 2016, it has been used in the market to realize the Internet of Things vision of modern connected cities. From Germany, Spain to Norway, a number of field tests have been successfully completed, proving that NB-IoT is an ideal solution for urban IoT applications (Figure 2).
Figure 2 NB-IoT application category
One of the main tasks of the Internet of Things is to promote effective monitoring and distribution of resources to achieve a smarter and more efficient world. But the problem with traditional Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular technology is that their transmission distance, power consumption, and cost characteristics cannot truly achieve this vision.
NB-IoT is able to play its strengths in a metropolitan environment, most importantly because it has features that complement traditional wireless technologies. It provides the transmission distance of cellular technology, the cost-effectiveness of Bluetooth, and unmatched indoor penetration, so that signals are not affected by obstacles and can be transmitted without interruption.
Wisdom scale
In Spain, local water company Aguas de Valencia has used NB-IoT to reduce operating costs and improve management visibility. In Valencia and other parts of Spain, Aguas de Valencia manages more than one million water meters, each of which requires periodic readings of water use (Figure 3). At present, many public utility companies send employees to the site to copy data, but this practice is not only costly, but also unable to grasp the user's usage in real time.

Figure 3 Smart meter reading is one of the main applications of NB-IoT
Inspired by NB-IoT related reports, this technology allows the infrastructure to be managed by the cellular network provider, so Aguas de Valencia decided to try u-blox's NB-IoT technology in the most difficult areas, including only Concealed spaces with metal covers such as basements or sewers that are weak or without a cellular network coverage, and other areas that are difficult to reach with traditional wireless technologies.
The result is amazing. Each test mobile device is installed in a position where the gauge is normally placed, and the reading is no problem. Agua de Valencia can get up to 24 real-time information a day, without having to dispatch staff to the site. Since NB-IoT is a standardized technology supported by cellular network providers, Agua de Valencia does not have to worry about the wireless infrastructure needed to manage water meters. Moreover, the NB-IoT device has a battery life of more than 10 years, so system maintenance and operating costs can be minimized.
Smart parking
Everyone knows that it is a nightmare to find a parking space around the city. This is not only a problem of driving, but also a traffic problem in the metropolitan area. About 30% of the traffic jams in the city come from the traffic flow of finding a parking space. Therefore, the goal of smart parking is to solve the problem of finding a parking space, and to inform the driver where there is a parking space through wireless communication technology. In addition to assisting in the need for parking, smart parking can also indirectly reduce traffic congestion in the metropolitan area, driving away from busy roads.
Smart parking is not a new concept, but it has not been truly successful in the past due to various technical and economic issues. With proprietary wireless protocols, most of today's smart parking systems require operators not only to install parking sensors, but also to build a wireless infrastructure to connect each sensor and connect them to the Internet. This is not only expensive for operators but also technically complex.
NB-IoT solves these problems because each sensor can communicate directly with the cloud. Not only does this reduce system cost, but it also greatly simplifies deployment and requires only sensors to be installed in the parking lot. Because the device is powered by a battery and communicates wirelessly, no cables are required, plus it uses cellular technology and does not require a wireless router.
NB-IoT has great potential for smart parking applications and has been successfully tested and deployed around the world. For example, in January 2017, Q-Free launched a test program for the new smart parking sensor and worked with the world-renowned mobile operator Telenor and the Norwegian Public Roads Agency (NPRA). In addition, a number of smart parking test programs have been conducted in China, Spain, Germany and Japan.
Smart agriculture
In addition to providing strong coverage in the metropolitan environment, NB-IoT can play a significant role in smart agriculture. Other wireless technologies may not cover large areas, and NB-IoT's long range and cellular design make it ideal for precision agriculture applications, including irrigation, pest control, and temperature and humidity monitoring.
For agricultural applications, like smart parking and smart meters, the value of NB-IoT comes not only from its wireless coverage and low power consumption, but also because it is easy to deploy. Parking operators, utilities, and farmers are not interested in becoming an expert in wireless infrastructure. They only want networking solutions to work.
Solve the bottleneck in the last ISM
Although NB-IoT completed the standard setting in June 2016, its acceptance is rapidly increasing. Currently, mobile network operators around the world are deploying NB-IoT networks from Spain to Norway, South Korea and Japan. NB-IoT is rapidly gaining popularity with the wireless IoT standard, which will bring excellent benefits to network providers and device manufacturers.
One reason for the rapid deployment of NB-IoT is because the build process is very easy. Many network providers only need to build NB-IoT through a software upgrade in their infrastructure. Because each base station can hold up to about 100,000 units, there is no need to worry about network capacity issues compared to other high-bandwidth technologies.
Network vendors supporting NB-IoT are profitable because NB-IoT can bring them a revenue source for the Internet of Things. While other low-power WAN technologies that are independent of cellular technology are also being developed, NB-IoT is being developed in conjunction with major telecom operators to enable them to provide network coverage in a contractual manner.
For device manufacturers, the rapid adoption and standardization of NB-IoT allows them to design compact, low-cost IoT devices that are easy to deploy and sell. The support of major network operators, as well as the cellular features, make NB-IoT ideal for wireless IoT technology regardless of compatibility or coverage.
Although there are a variety of wireless protocols competing with each other in an attempt to snatch the market for linking IoT devices to the cloud, only NB-IoT combines wireless performance, economic benefits and ease of use, making it ideal for mainstream IoT applications. Even with the ability to provide powerful wireless performance in a metropolitan environment with long distances, low power consumption, and ease of deployment, NB-IoT will surely become the "last mile" solution for the Internet of Things.

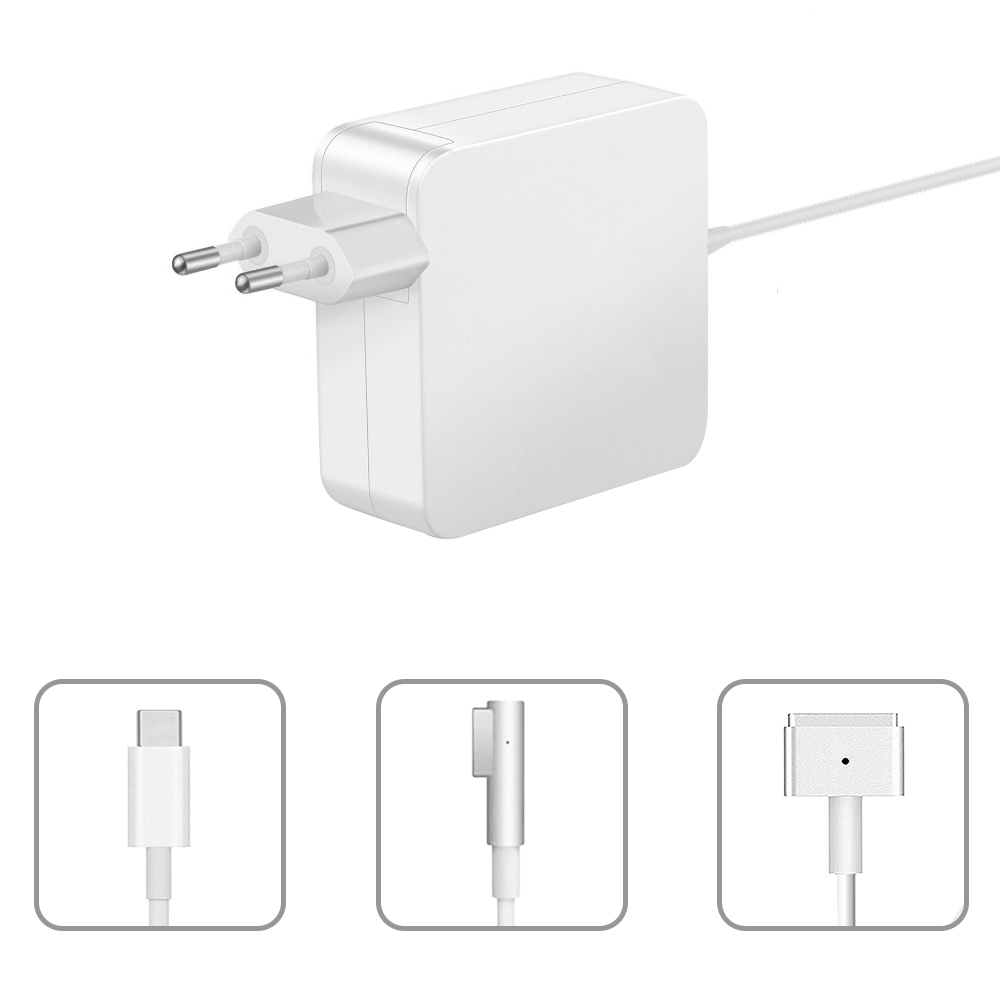
The 60W Macbook Charger with MagSafe1 or Magsafe 2 Power Adapter has a magnetic DC connector, so if someone trips on it, the power cord disconnects harmlessly, keeping your MacBook Air safe. It also helps prevent the cable from fraying or weakening over time. Additionally, the magnetic DC helps guide the plug into the system for a quick and safe connection.
60W Apple charger usb c,60w charger macbook air,macbook 60w charger
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.waweis.com