Digital TV is a digital signal that processes, quantizes and encodes traditional analog TV signals into digital signals represented by binary numbers, and then processes, transmits, records, stores, monitors and controls various functions. End-to-end system. It is this all-digital feature that allows us to use a variety of digital technologies to enable TV devices to achieve higher technical performance than the original analog TV devices. Conditional access is to encrypt and transmit information such as video, audio and data. The process of receiving a decryption by a legitimate user. Conditional access to the expansion of the management methods of broadcast and television operators enables operators to authorize and control the information received by users. He is considered to be the single business model in which the broadcasting and television industry breaks the advertising-based revenue and realizes the technical basis for diversified operations. And powerful tools.
This article refers to the address: http://
1 Principle and safety guarantee system of conditional access system
1.1 Principle of Conditional Access System
From the implementation process, you can basically understand the basic technology needed to integrate a conditional access system. The first is the database system that records the user's authorization status, that is, the user management system in the CA system, and the second is the database system that records the service authorization control situation, which is the program management system; and the system for service scrambling/descrambling control; Management and transmission system technology, smart card reading and writing technology, etc. These are the indispensable technologies for integrating a CA system. The encryption, decryption and password management transmission of information is the core of the CA system. The process of adding/decrypting information closely connects all the above-mentioned technologies into one. The CA system is shown in Figure 1.
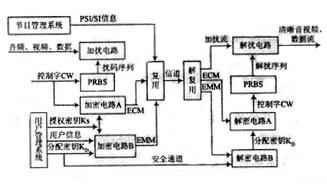
Figure 1 Principle of common conditional access system
As can be seen from Figure 1, the commonly used CA system generally has a three-layer encryption system.
The first is the scrambling of audio and video and data streams. It is the process of encrypting the information stream by the scrambling sequence. The scrambling code sequence is a pseudo-random binary sequence. It has a power spectrum characteristic of an approximate random sequence, except that it has a period, but the period is very long, usually hours or even days. The PRBS refers to the scrambling code sequence generator in FIG. The initial condition of the generator is controlled by the control word (CW), and in the case where the initial conditions are known, the generated scrambling code sequence can be inferred. Here CW plays the role of "seed", as long as CW is obtained, the system is cracked. So how to send CW security to the receiving end becomes the core of the CA system. The latter two-fold encryption process is to achieve the secure transmission of CW and achieve the purpose of authorization control.
To achieve confidentiality, the control key CW is encrypted using the authorization key KS to form authorization control information (ECM), which is multiplexed into the transport stream. At the same time, the authorization key KS is encrypted using the distribution key KD to form authorization management information (EMM), which is also multiplexed into the transport stream. The system confirms the authorization key KS of the service to be KS1 through the confirmation of the user management system, but the authorization management information EMM encrypted by the KD is still sent to the user, and the user can decrypt the KS but cannot enjoy the business.
The above encryption process can be seen that an authorized receiver uses the relevant services to obtain EMM and ECM in turn. The extraction of such information depends on the PSI/SI information (special program information/program information) provided by the program management system. The PMT table is for the encryption of the program, and it also contains CA_SySTem_Id information for indicating which CA system encryption and EMM_Pid are used to inform the user how to search for the ECM. CA_System_Id can uniquely identify the CA system. The content assigned to the user's smart card contains this content. The conditional receiving process of the client starts from reading the CA_System_Id in the card, and obtains the corresponding EMM. After the ECM, the decryption and descrambling work is pressed. The reverse order of the sender begins.
The composition of the CAS includes: a user management system SMS, a service information generation system SIG, a program management PMS/SI editing system, a program scheduling processing EIS, a user authorization management system SAS, a conditional access CA, and the like. There are two main blocks: one is the SMS that manages the user, and the other is the CA that manages the program. CA is mainly divided into two parts: one is the signal scrambling part, which is a random code generated by a random code generator (called the control word CW) to control the scrambler to scramble the signal; the second is the encryption part. In order for the scrambled signal to be successfully descrambled at the receiving end, the receiving end must also have a control word identical to the scrambling end to control the descrambler. Therefore, the front end CW is transmitted to the receiving end if it is directly transmitted. It will be easily intercepted by hackers and make CAS useless. To this end, CW is encrypted and transmitted. This encryption is a multi-layer encryption mechanism, which increases the security of CW transmission, directly to the first layer of CW encryption. The generated ciphertext is called the authorization control information ECM, and is transmitted together with the scrambled code stream through the multiplexer. The ECM also contains information such as time, program price, program authorization control, etc., so the ECM is program-oriented management information. The key encrypted for CW is called the work key SK. SK is usually called the monthly key. It is changed once a month. Every time SK is changed, the system must re-authorize all users. The second layer encryption is performed by encrypting the SK with a program key PDK, and the generated ciphertext and the authorization information acquired from the SMS form the authorization management information EMM generated by the SAS. The EMM also contains the smart card number, the authorization time, User authorization information such as authorization level. This information is mainly to complete the authorization of the user, so the EMM is the management information for the user. The EMM authorizes the user at what time to watch and see what channel, and it is also transmitted through the multiplexer together with the scrambling code stream. The most basic encryption system of CA.
1.2 Security measures for CA systems
Security is the soul of conditional reception. The design of the principle of CA system not only reflects the operation security system but also reflects the countermeasures that can be used after the system is cracked. This robust security system is manifested in three aspects:
The CW transformation mechanism CW is the basis of the system architecture and is the core of conditional reception. CW is generally 60 b, so his coding space is known, so CW cannot be unchanged. In practice, it changes once every 2~10 s. If it is a CW attack, even if you get a CW, his life span is very limited. This change mechanism makes the use of CW stealing meaningless.
SK's upgrade system's algorithmic attack on encryption circuit A is currently the most commonly used method of cracking, and his success rate is also the highest. If the CW is solved by the ECM if the encryption algorithm and SK are known, the change mechanism of the CW also loses its effect. Robust encryption algorithms are the key to security. If the algorithm is cracked, the current SK must be upgraded to make the pirated card useless, so SK's large enough coding space is also a necessary condition to improve the system security level.
Smart Card Circuit Design The smart card is a chip with built-in microprocessor, RAM, ROM and E?2PROM, storing the distribution key, decryption algorithm and operating program. The key to the distribution is the last security line of the entire CA system. His importance is self-evident, so the circuit of the smart card, especially the ROM that stores the distribution key, is designed to be unscannable. Once detected, the data in the ROM is automatically erased. except. At the same time, in order to prevent the operation program from being copied, the storage area is segmented to save the application, and each program has a different security code.
No encryption algorithm is never cracked. At this stage, many well-known CA systems have been cracked records, basically the second and third ways of attack. Now the most effective way is to replace the smart card and completely update the two encryption algorithms. Although this method is relatively expensive, it is the most effective way to increase the cracking cycle.
2 two ways to achieve
As can be seen from the principle, the most important feature of the CA system is information confidentiality. In fact, the encryption algorithms used by many CA systems are private to each system operator and are absolutely confidential. This characteristic determines the exclusivity and non-universality of each CA system. To solve this problem, the European DVB Standards Organization defines two types of conditional access systems, simulcrypt and multicrypt.
2.1 Same-density condition receiving system
If multiple CA systems are added at the sender, the same-mode approach is based on the commercial protocol between the operators, using the same control word generator and scrambling code generator, and scrambling the signal using a common scrambling algorithm. The difference between the different systems begins with the encryption of the CW, which uses its own encryption algorithm to encrypt the CW and the authorization key KS. User management systems can be public or separate. The program management system will describe the CA_System_Id and EMM and ECM index information of various CA systems in one-to-one correspondence in the PSI/SI information. The schematic diagram is shown in FIG. 2 .
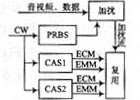
Figure 2 Principle of the same dense CA system
A receiving decoder (STB) integrated with one of the CA systems reads the corresponding CA_System_I d from the inserted smart card, obtains the EMM according to the identifier, and extracts the specific information and sends the specific information back to the smart card.
Two sets of private decryption algorithms are integrated in the smart card, corresponding to the encryption algorithm of the EMM and ECM generated by the front end, so that the CW is obtained and sent to the receiving decoder STB. The descrambler integrated with the universal descrambling algorithm is included in the decoding chip of the STB. With this descrambler, the original signal can be recovered. Users can watch the program as long as they are authorized by one of the confidential systems. In this way, the signal is added and descrambled by using a general algorithm, so the communication security in this way is guaranteed by the smart card, and the two-layer private encryption circuit is the key. This approach requires the conditional access system to be embedded in the receiver.
2.2 Multi-density conditional receiving system
Understand the principle of the same secret, the principle of the multi-dense system is easy to understand. The difference between them is that different CA systems operators use different CWs, different scrambling code generators and scrambling algorithms for multi-density systems. Similarly, the latter two layers of encryption algorithms are also private. This makes it impossible for the receiving end to use the common descrambling algorithm circuit in the decoding chip, but the conditional receiving module solves this problem well. The command interface between the module and the host provides a communication method between the module and the host part without requiring the host to understand the specific details. The application of this universal interface enables a set-top box to use modules of multiple CA operators, that is, to watch programs controlled by different CA systems.
The principle of the same dense and multi-density mode is shown in Figure 3.
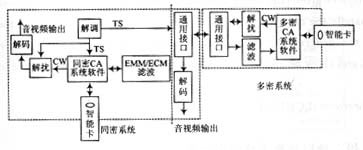
Figure 3 Principle of receiving the same dense and multiple dense CA system
3 Comparison of the two methods
3.1 Communication costs
In the same-dense mode, the TS stream carries the EMM and ECM of all applied CA systems, which increases the difficulty of multiplexing at the transmitting end (each EMM, the ECM stream must be assigned a unique PID, and some synchronization requirements), Communication bandwidth requirements have also been increased. A TS stream usually has only one set of CA system applications, so the amount of information is smaller than the same type.
3.2 versatility and characteristics of set-top boxes
The basic function of a digital set-top box is to receive digital TV broadcasts, as well as all broadcast and interactive multimedia applications, such as:
(1) Electronic Program Guide (EPG). Providing users with an easy-to-use, user-friendly, and quick-access method to watch programs, which allows users to see TV shows that will be played on one or more channels or even on all channels;
(2) High-speed data broadcasting. Can provide users with stock market quotes, ticket information, electronic newspapers, popular websites and other news;
(3) Software online upgrade. Software online upgrade can be seen as one of the applications of data broadcasting. The data broadcast server broadcasts the upgrade software according to the DVB data broadcast standard, and the set top box can identify the version number of the software, receive the software when the version is different, and update the software stored in the memory;
(4) Internet access and email. The digital set-top box provides easy Internet access through a built-in cable modem. Users can go online and send emails through the built-in browser of the set-top box. At the same time, the set-top box can also provide various interfaces to connect with the PC, and connect to the Internet by using a PC;
(5) Conditional reception. The core of conditional reception is scrambling and encryption, and the digital set-top box should have descrambling and decryption capabilities. In summary, so far, a variety of value-added services have been developed around the three core functions of digital video, digital information and interactive applications for digital set-top boxes.
Set Top Box, in a broad sense, any network terminal device connected to a TV set can be called a set-top box. Analog channel adders based on cable TV networks, analog channel decoders, "Vilas" Internet set-top boxes that connect telephone lines to TV sets, integrated receiver decoders (IRD) for digital satellites, digital terrestrial set-top boxes and cable TV digital set-top boxes can be called set-top boxes. In a narrow sense, if only digital devices are used, they are divided into digital satellite set-top boxes (DVB-S), European standard digital terrestrial set-top boxes (DVB-T), national standard digital terrestrial set-top boxes (DMB-TH), and cable digital set-top boxes. (DVB-C). According to the function, it can be divided into one-way set-top box, two-way set-top box, and IPTV set-top box.
As can be seen from the schematic diagram, since the specific CA system software must be integrated in the set-top box of the same-density system, the receivers of the same-density mode integrate the CA-related software and hardware systems into one CI module, and the set-top box can apply any conformity. The module of the universal interface standard can therefore be applied in a variety of CA systems. The versatility is more dense than the same.
3.3 Security
The multi-mode control word CW form and the 3-layer encryption algorithm are both private. To solve at least two sets of encryption algorithms are needed, the CW coding space used by the same-secret algorithm is public and the used descrambling algorithm is universal. So, he has one layer of anti-cracking defense than the multi-dense system. Thirdly, since the communication interface between the set-top box and the smart card supporting the same-density system is more open than the same-secret system, the thief can easily steal communication data from the communication interface between the host and the card for analysis or for activating another decoder. The purpose of piracy. The fact that most currently cracked systems use this approach. Therefore, in the interface security, the same dense system is also worse than the multiple dense system.
3.4 Cost
Although the multi-density system has the above two advantages, he needs to pay the cost. Now the market price of a module is at least 300~400 yuan, and some are more than 1,000 yuan. And if you only use one module, then there is no point in using multiple secrets. Therefore, the set-top box of the multi-density system generally costs more than the same density, and the transmitting end also consumes more equipment costs. At present, China is in the initial stage of digital TV development. Due to cost reasons, the same-density system is still the mainstream of domestic digital TV. However, from the perspective of development, the multi-density system will replace the same dense system.
4 CA system development status
At present, the international conditional access systems mainly include the M_Crypt system and π_s ys system of IRDETO, the Viaccess system of France Telecom, the NDS system of NDS of the United Kingdom, and the Mediaguard system of Canal+ of France. , as well as the Nagra system. Domestically, there are mainly Tsinghua Tongfang, Zhongshilian (joint venture with Philips), and computing technology. The foreign CA system has experienced many years of development, the technology is relatively mature and forms a certain market. The domestic CA system research started relatively late, the starting point is relatively high, and it draws on the experience of foreign countries. It has developed rapidly and has formed a domestic market with a large scale. At the same time, actively carry out the same secret with foreign CA systems, the above several well-known domestic CA operators have achieved the same secret with IRDETO, NDS. This kind of competition and simultaneous development has taken shape in the domestic digital TV industry.
Black Light Tube,Blb Tube,Blb Bulb,Blb Lamp
Changxing leboom lighting product CO.Ltd. , https://www.leboomuv.com