Newton ring, also known as "Newton Circle." Optically, the Newton ring is a thin film interference phenomenon. An interference pattern of light is a concentric ring of light and dark. For example, a convex surface of a convex lens having a large radius of curvature is in contact with a flat glass. When exposed to sunlight or white light, the contact point is a dark point surrounded by a number of bright and dark colored rings; When the color light is illuminated, it appears as a number of solid circles of light and dark.
The distances of these circles are unequal and gradually narrow as the distance from the center point increases. They are interference fringes formed by the interference of light reflected on the spherical surface and the plane. The convex surface of a convex lens with a large radius of curvature is in contact with a flat glass. When exposed to sunlight or white light, the junction point is a dark spot surrounded by bright and dark colored rings. When the color light is illuminated, it appears as a number of solid circles of light and dark.
The distances of these circles are unequal and gradually narrow as the distance from the center point increases. They are interference fringes formed by the interference of light reflected on the spherical surface and the plane.

The principle of Newton's ring is not complicated, it is a kind of interference pattern of light. It was first observed by Newton in 1675. A flat convex lens with a large radius of curvature is placed on a glass plate, and the lens and the glass plate are illuminated by monochromatic light, and some concentric rings of light and dark are observed. The distribution of the ring is intermediate, the edge is dense, and the center of the circle is at the contact point. The center of the Newton's ring seen from the reflected light is dark, and the center of the Newton's ring seen from the transmitted light is bright. If it is incident with white light. A colored ring will be observed. The Newtonian ring is a typical isometric film interference. A round-shaped dome-shaped air film having a uniform thickness is formed between the convex spherical surface of the convex lens and the glass plate. When the parallel light is directed perpendicularly to the plano-convex lens, the two beams reflected from the upper and lower surfaces of the pointed air film are superposed on each other. Produce interference. The thickness of the air film at the same radius of the ring is the same, and the difference in the optical path of the upper and lower surfaces is the same, so the interference pattern is annular. This interference of the same interference fringes produced by the same thickness of film is called equal thickness interference.
An important finding of Newton in optics is the "Newtonian ring." This was proposed by him when he further examined the color of the soap bubble film studied by Hook. Although Newton discovered the Newton's ring and made accurate quantitative measurements, it can be said that it has reached the edge of the fluctuation of light, but because of the excessive preference for his particles, it is impossible to explain this phenomenon correctly. In fact, this experiment can be one of the strong evidences of the fluctuation of light. It was not until the early 19th century that the British scientist Thomas Young used the undulations of light to explain the Newton's ring experiment satisfactorily.
Newton's rings are commonly used in manufacturing: determining the surface of the lens, accurately examining the surface quality of the optical component, measuring the radius of curvature of the lens surface, and the refractive index of the liquid. It can also be applied to a spectrometer to separate the composite light into a composition of monochromatic light.
Newton ring gauge lens radius of curvature
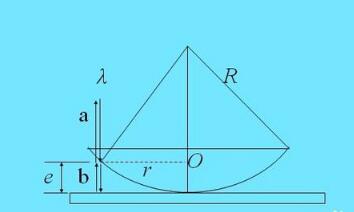
From the bright ring radius formula (6) and the dark ring radius formula (8) of the Newton ring meter, it is known that the radius of the j-th order interference dark fringe of the formed Newton's ring or the radius formula of the j-th order interference bright stripe is known. When λ is known, the radius of curvature R can be obtained by experimentally measuring jr or jr.
However, due to the inevitable dust or elastic deformation between the two contact surfaces in actual operation, the contact between the two optical elements cannot be a geometric point, but a circular spot. Therefore, it is not practical to directly calculate the radius of curvature by directly applying the formula to the ring pattern at the center of the Newton's ring.

Top flat Newton ring device measuring lens radius of curvature

Can be found:
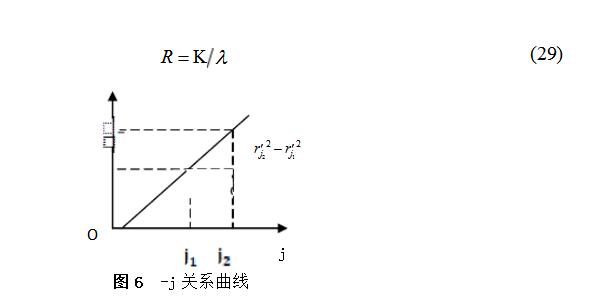
Measuring the radius of curvature of the lens on the top Newton ring device

Newton ring gauge to measure the refractive index of uniform light medium
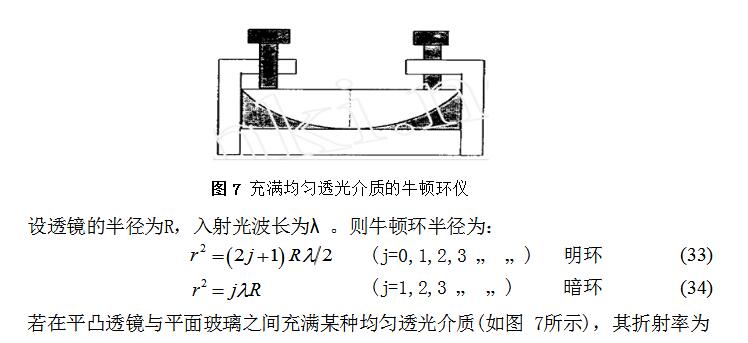

Deformed Newton ring device for measuring the refractive index of uniform transparent medium
The top-flat Newton ring deformation device and the top-type Newton ring deformation device measure the refractive index of the uniform light-transmissive medium in the same manner as the Newton ring device. Let the incident light wavelength be λ. Then their Newton's ring radius can be expressed as:

Newton ring gauge accurately detects the quality of optical components
When the optical element is not smooth or has impurities, when the Newton's ring is observed in the laboratory, it is sometimes found that the originally rounded Newton's ring is locally deformed, and is generally partially concave in the Newton's ring. What is the reason? A qualitative theoretical analysis of this experimental phenomenon is given below. In the case of normal incidence of monochromatic light, the interference conditions of Newton's ring and dark lines are:
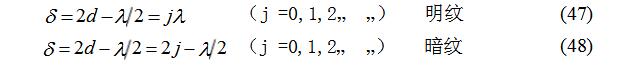
It is characterized by the same thickness d, the optical path difference is equal, forming the same level of interference fringes. As shown in Figure 8, but when the optical element
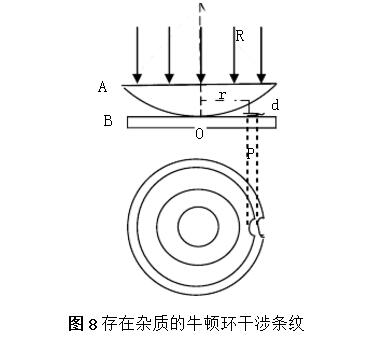
When the surface of the piece is not smooth, the thickness of the intermediate medium will change slightly; and when the surface has impurities, the refractive index of the impurity is generally larger than the refractive index of the air, causing an additional optical path difference. In both cases, the interference fringes are distorted. Set the micro-neighbor of a point P on the flat glass plate B to be non-standard (having impurities or non-smoothness), the refractive index is n, and the linearity along the direction of the ray is a, then the optical path difference of the two reflected light at the point P for

Deformed Newton ring device accurately detects the quality of the surface of the optical component
In the top flat Newton ring deformation device or the top-type Newton ring deformation device, in the case of normal incidence of monochromatic light, the interference conditions of Newton's ring and dark lines are:
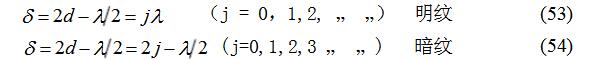
It is characterized by the same thickness d, the optical path difference is equal, forming the same level of interference fringes. However, when the surface of the optical element is not smooth, the thickness of the intermediate medium will change slightly; and when the surface has impurities, the refractive index of the impurity is generally larger than the refractive index of the air, causing an additional optical path difference. In both cases, the interference fringes are distorted. It is assumed that there is a problem in the tiny neighborhood of a point P on the plano-convex lens B (having impurities or non-smoothness), the refractive index is n, and the linearity of the two reflected light at the point P is a, and the optical path difference of the two reflected light at the point P is :

Metals Customization Products.Connector, hardware accessories, connection terminals, shrapnel, metal stamping parts, round hole machined pin.
Metals Customization Products
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkconn.com